Frequency
Period
Amplitude
Phase
Wavelength
Speed
Wave Front
Frequency
Frequency is the number of vibrations per unit of time. The SI Unit of time is hertz (Hz) and symbol for frequency is “f.” 1 Hz= 1 s^-1.  This picture shows different frequency waves.
This picture shows different frequency waves.
Period
Period is the time required for one complete vibration. The symbol for Period is “T” the SI Unit is second and it is the reciprocal of frequency T=1/f
 This shows one period of a graph.
This shows one period of a graph.
Amplitude
Amplitude is the maximum Displacement of a particle of the medium from its rest position. Another name for amplitude is height (of the wave).
Examples:
- Light wave amplitude
- Brightness
- Sound wave
- Amplitude
- Loudness
Phase
Waves that cross paths while traveling in the same direction are considered to be in phase
Phases have
o The same displacement from the rest position
o The same direction of motion
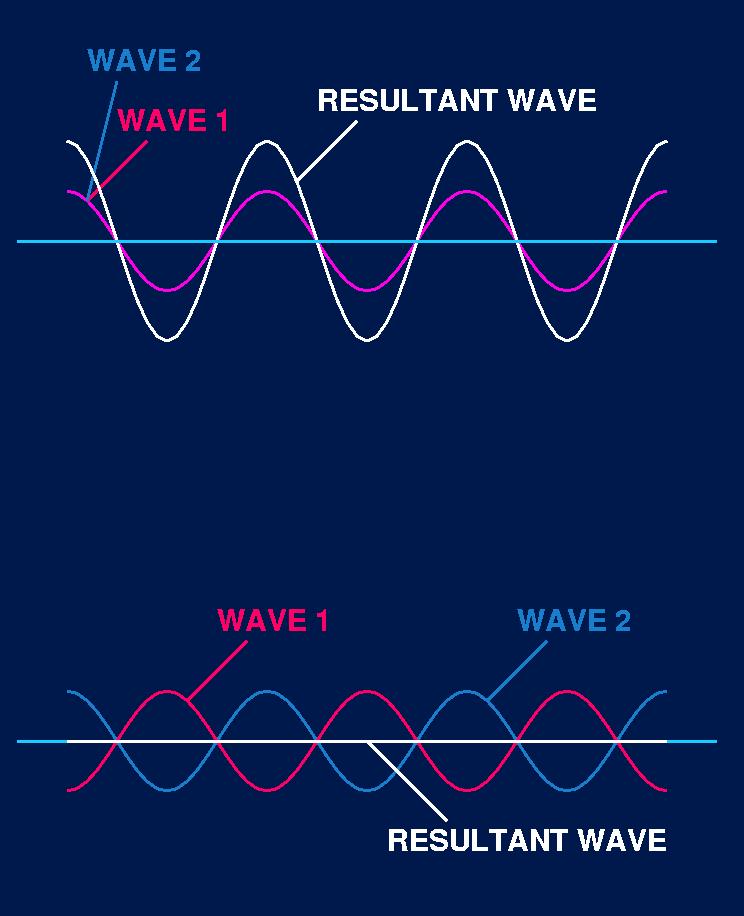
Here wave 1 and wave 2 are said to have a phase difference of 2(pi), or simply are in phase, because both waves have the same wavelength and rise and fall together. Any two waves with a phase difference of a multiple of 2(pi) are in phase.
Wavelength
- The wavelength of a wave is the distance between any two adjacent corresponding locations on the wave
- The distance is usually measured in one of three waves
- Trough to trough
- From the start of a wave cycle to the next starting point
- Crest to next crest
- Shown below:
Speed of a Wave
- The speed of a wave equals the product of wavelength and frequency
- Examples
- We see the bat hit the ball before the crack is heard
- Shouting and hearing your echo
Wave Front
- A wavefront is a line or surface, in the path of a wave motion
We also had a worksheet for homework. It's called waves #1!
